Google Cloud and MITRE make it easier for businesses to threat-hunt in their cloud environments
The new pre-built queries aim to make it easier to navigate cloud security for organisations without the deep understanding that's required to effectively manage threats


Google Cloud announced an extension of its partnership with security company MITRE to further its efforts in making cloud security easier to deploy for every organisation.
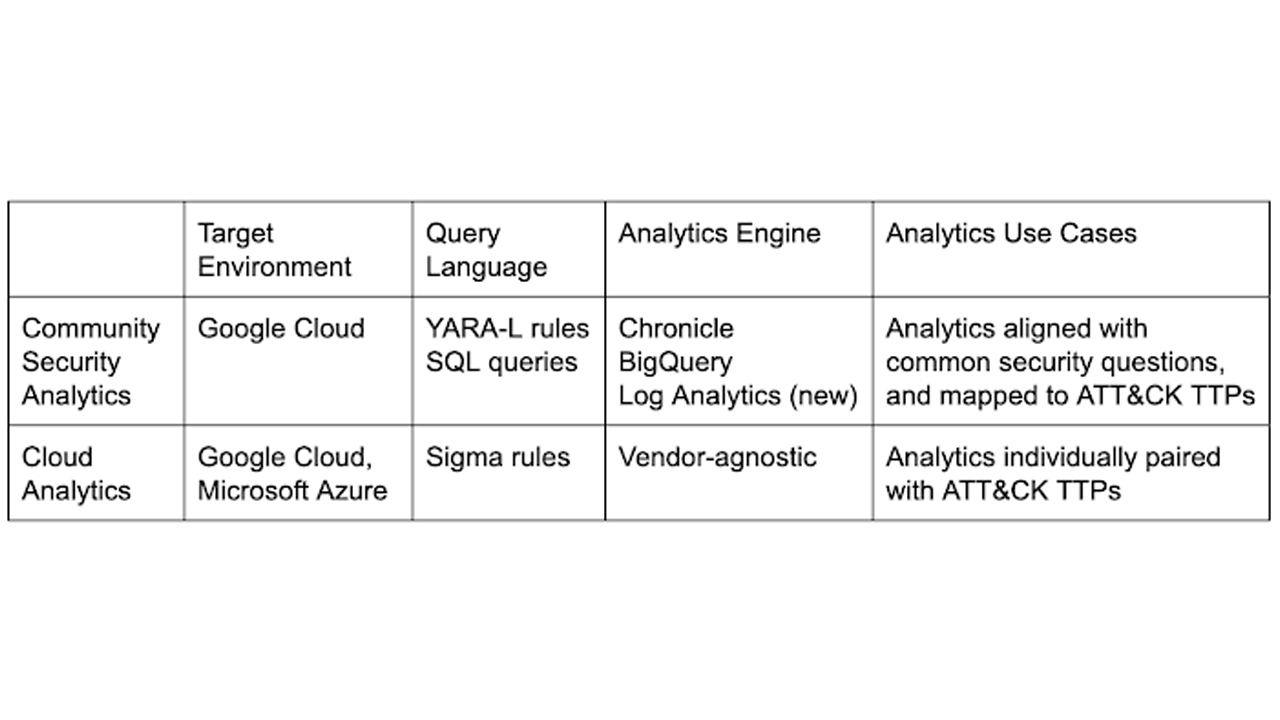
The Cloud Analytics project is a community-driven initiative to provide security analytics resources to the wider community and builds on the existing work the two companies have done with the Community Security Analytics (CSA) project.
Cloud Analytics provides organisations with a set of pre-built queries that aim to make threat hunting for cloud-specific security vulnerabilities less complex than it already is.
The queries are customisable but come already tailored to known tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) adopted by threat actors that target cloud environments.
Google Cloud said the task is currently difficult for many organisations because it requires a deep knowledge of diverse security signals and a familiarity with adversary behaviours in cloud environments, among other factors.
Co-developed in 2021 by Google Cloud, MITRE Engenuity Center, and other industry partners, the CSA is similar to Cloud Analytics in that it provides a set of open-sourced queries to improve threat hunting, but does so for different technologies.
For example, CSA’s target environment is Google Cloud Platform (GCP) only, whereas Cloud Analytics is for GCP and Microsoft Azure.
Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report - the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
The open-sourced query languages and target analytics engine also differ with CSA using YARA-L rules and SQL queries as the languages, and the analytics engines being Chronicle, BigQuery, and more recently, Log Analytics.
Cloud Analytics uses Sigma rules and adopts a vendor-agnostic approach to analytics engines. Sigma rules allow organisations to translate these into “vendor-specific search queries such as Chronicle, Elasticsearch, or Splunk using Sigma CLI or third party-supported uncoder.io, which offers a user interface for query conversion”.
Google Cloud said both community projects complement each other and provide users with the best opportunity to maximise coverage of the MITRE ATT&CK framework - a long-running guideline for classifying and describing various cyber attacks.
Although the queries are already provided by the two projects, Google Cloud said organisations are expected to adopt a do-it-yourself approach and finely tune them specifically for each organisation’s environment.
To get started with the open-source project, all the files are hosted on GitHub, including the complete set of Sigma rules, the associated adversary emulation plan required to trigger the rules, and a development blueprint to help inform users how to create bespoke Sigma rules to further increase cloud security.
“The Cloud Analytics project aims to make cloud-based threat detection development easier while also consolidating collective findings from real-world deployments,” said Google Cloud in a blog post.
“In order to scale the development of high-quality threat detections with minimum false positives, CSA, and Cloud Analytics promote an agile development approach for building these analytics, where rules are expected to be continuously tuned and evaluated.”
Google Cloud has been strong in its messaging over the past year, informing customers that cloud security threats are increasing.
Cryptomining has been a particularly troublesome threat, it has previously said, with 86% of compromised GCP instances in 2021 leading to miners being dropped into customers’ environments.
In most cases (58%), it only took an average of 22 seconds for attackers to drop a miner after having gained access to an environment.
Following the discovery, Google Cloud launched Virtual Machine Threat Detection (VMTD) in February 2022 to automatically detect cryptomining attacks, among other threats like data exfiltration and ransomware.

Connor Jones has been at the forefront of global cyber security news coverage for the past few years, breaking developments on major stories such as LockBit’s ransomware attack on Royal Mail International, and many others. He has also made sporadic appearances on the ITPro Podcast discussing topics from home desk setups all the way to hacking systems using prosthetic limbs. He has a master’s degree in Magazine Journalism from the University of Sheffield, and has previously written for the likes of Red Bull Esports and UNILAD tech during his career that started in 2015.

