What is YAML?
New programmers thrust into the industry may be left asking themselves ‘what is YAML?’ - here's everything you need to know


YAML is a popular programming language responsible for coding configuration files, and so is often used in tandem with many other languages.
For example, Google-developed Flutter framework for Dart and Python both use YAML (.yaml) when writing configuration files for application projects. It's also popular among cloud engineers due to its applicability in formatting containerized files.
Unfortunately, it's not the most welcoming language for new users, and slight formatting errors can completely break the code. YAML requires a very precise number of spaces across multiple lines to show how data sits in a hierarchy.
It’s not always easy for a newcomer to detect where there is a spacing error since most integrated developer environments don’t throw errors for broken YAML code, which at times can disrupt the development process.
What is YAML and when was it created?
YAML was first released in May 2001 and has remained a mainstay in the world of programming and coding for more than two decades now.
YAML is actually an initialism – it originally stood for 'Yet Another Markup Language’ but was later renamed to ‘YAML Ain’t Markup Language’ to better emphasize the fact YAML is a language used for data configuration, rather than for documentation.
The language has remained highly popular thanks to its human-readable nature, with a syntax that's highly intuitive. It’s deemed a more readable and developer-friendly version of JSON or XML.
Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report - the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
YAML syntax explained
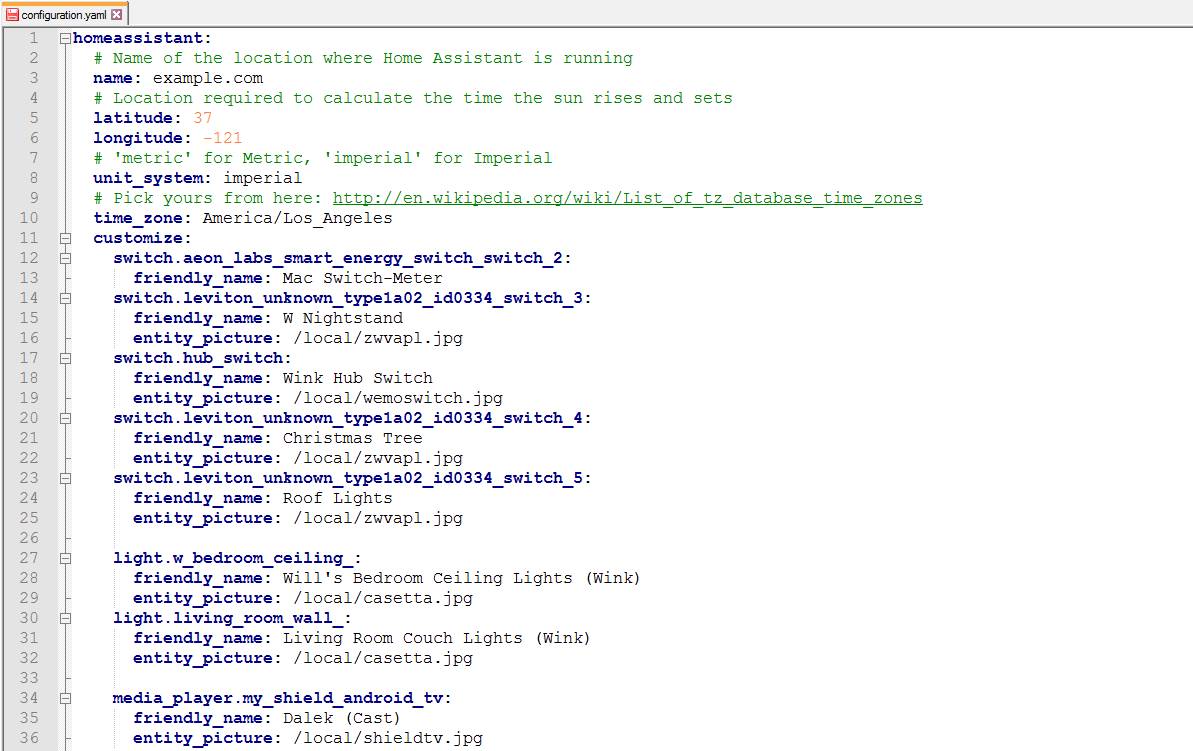
YAML includes features inspired by various patterns and tools embedded in other programming languages in order to ease the process of reading and writing code.
For instance, indentations and new lines may be used to structure code so the way it appears on your screen reflects how it works in practice, such as in Python. You can also configure how deep indentations are to ensure it’s as readable for you as possible, as long as you retain consistency across the code you’re writing.
You won’t be able to use a tab character, however, which does dodge the compatibility issue of different operating systems processing tabs in different ways. This also negates the tabs versus spaces issue.
Coders may use YAML to adopt tighter formatting in which the two main data types, lists and arrays, also known as maps, are signified by the [ ] and { } figures. Effectively, this renders YAML a superset of JSON, though it’s outlined for machines, and not people, to read. YAML also includes features absent from JSON, such as comments, the latter of which hasn’t been created to support.
The data types might also be nested, as in Pearl, to show more complex structures. There are also features taken from C, HTML and MIME, as well as mail headers, with colons used to denote key:value pairs.
The space function is also included so you wouldn’t need to encase strings and numbers with quotation marks. Types such as integers, clots and Booleans are automatically detected, and there’s support for ISO-formatted dates and times, although you can also establish your own data types.
Structures let you store multiple documents in a single file or refer to content in one part of the document from elsewhere using an anchor (which also lets you duplicate or inherent properties).
That means it's much more flexible than JSON where the hierarchy is fixed, with each child node having only one parent node and while there's a similar option in XML the YAML parse automatically expands the references.
That way you get a file that's easier to read and you avoid potential errors copying and pasting parameters where only a handful of things change between different instances, but external systems don't need to be told about the structure of the YAML file.
Why use YAML? The benefits explained
YAML is functionally quite easy to use. As the formatting is straightforward and you don't have to worry about closing tags, brackets or quote marks, you can edit YAML in simple text editing tools, and subsections of YAML files are often valid YAML.
RELATED RESOURCE

But there are also plugins to add YAML support to common IDEs like Visual Studio Code and Atom; these can use the YAML Language Server provide autocomplete and Intellisense, and there are several YAML linters to check code for correctness.
You can't write YAML that validates itself the way XML documents can do, based on schema, but if you need to define a schema for your YAML there are languages that let you do that.
The combination of YAML and JSON Schema can be powerful: VS Code, the DocFX static web site generator and even the schema for Microsoft's Q# Quantum Chemistry library use them together to achieve a more human-readable version of JSON.
Using YAML files has advantages over typing in command line options: you can create much more complex structures in YAML and you don't have to deal with long and unwieldy strings of parameters. And because they're files, you can check them into source control systems, track versions and changes.
As YAML also treats lines as information, it works better with git-based systems for tracking changes than JSON. That makes it easier to treat configuration as code that you manage, test and consume the same way you do all your other code.
Why wouldn't you use YAML?
Although functionally it's quite intuitive, it's not an easy language for newcomers.
Even small mistakes made when typing YAML code can lead to file-breaking errors. It was designed to be more easily readable by humans and its syntax reflects that, but developers often run into annoying cases where they have to spend time looking for the slight formatting error that won’t allow them to compile their codebase.
Since YAML is more readable than JSON or XML, reading through a YAML file will more likely lead to finding errors than in other languages. With the kind of configuration you perform in YAML becoming more relevant to the adoption of DevOps, configurations you're specifying may become more complex and may demand more expertise - regardless of the language you’re writing them in.
Arguably, there are better languages, such as TOML, but these haven’t been adopted as widely, so YAML is the language more developers will face.
Higher-grade tools will always be easier to work with versus reading and writing YAML files, and there’s a swelling choice of those for Kubernetes. This choice of tools ranges such as Helm, which streamlines installing and managing Kubernetes apps to managed cloud services, to the kubectl command line.
Tools such as Pulumi, which use familiar programming languages like JavaScript or PowerShell, also fall into this camp.
Ultimately, YAML is a configuration format that's present in so many widely-used tools and projects that it’s worth familiarizing yourself with it, and understanding its benefits and drawbacks.

Keumars Afifi-Sabet is a writer and editor that specialises in public sector, cyber security, and cloud computing. He first joined ITPro as a staff writer in April 2018 and eventually became its Features Editor. Although a regular contributor to other tech sites in the past, these days you will find Keumars on LiveScience, where he runs its Technology section.
-
 Coding vs programming vs scripting: What’s the difference?
Coding vs programming vs scripting: What’s the difference?In-depth Your comprehensive guide to the important distinctions between coding, programming, and scripting
-
 The best C++ courses to kickstart your software development career
The best C++ courses to kickstart your software development careerIn-depth Some of the best C++ courses available today for landing a new job, from entry level courses to full certificates
-
 The 9 best courses for R
The 9 best courses for RIn-depth Whether it’s data science, machine learning, and statistics you are interested in, there’s a course that will teach you R
-
 The best online Python courses
The best online Python coursesIn-depth A snapshot of some of the best online Python courses around, offering the tools you need to start or develop your coding career
-
 Tech leaders share how to break into the tech industry
Tech leaders share how to break into the tech industryIn-depth “You have to feel like a true member of the IT world before you actually become a member"
-
 Can I become a coder?
Can I become a coder?In-depth Our fortysomething writer rekindles his childhood passion for coding – but can he teach himself Python from scratch?
-
 The IT Pro Podcast: Why cool kids code with COBOL
The IT Pro Podcast: Why cool kids code with COBOLIT Pro Podcast Skills and development isn’t just about cloud - sometimes it’s about keeping legacy systems going too
-
 The best free coding courses in the UK
The best free coding courses in the UKBest A list of some of the best free coding courses in the UK to kickstart your career in software development and programming

