The pros and cons of facial recognition technology
There are plenty of pros and cons of facial recognition technology, but is it really worth risking user privacy in the name of efficiency and security?
Rene Millman

Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report - the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
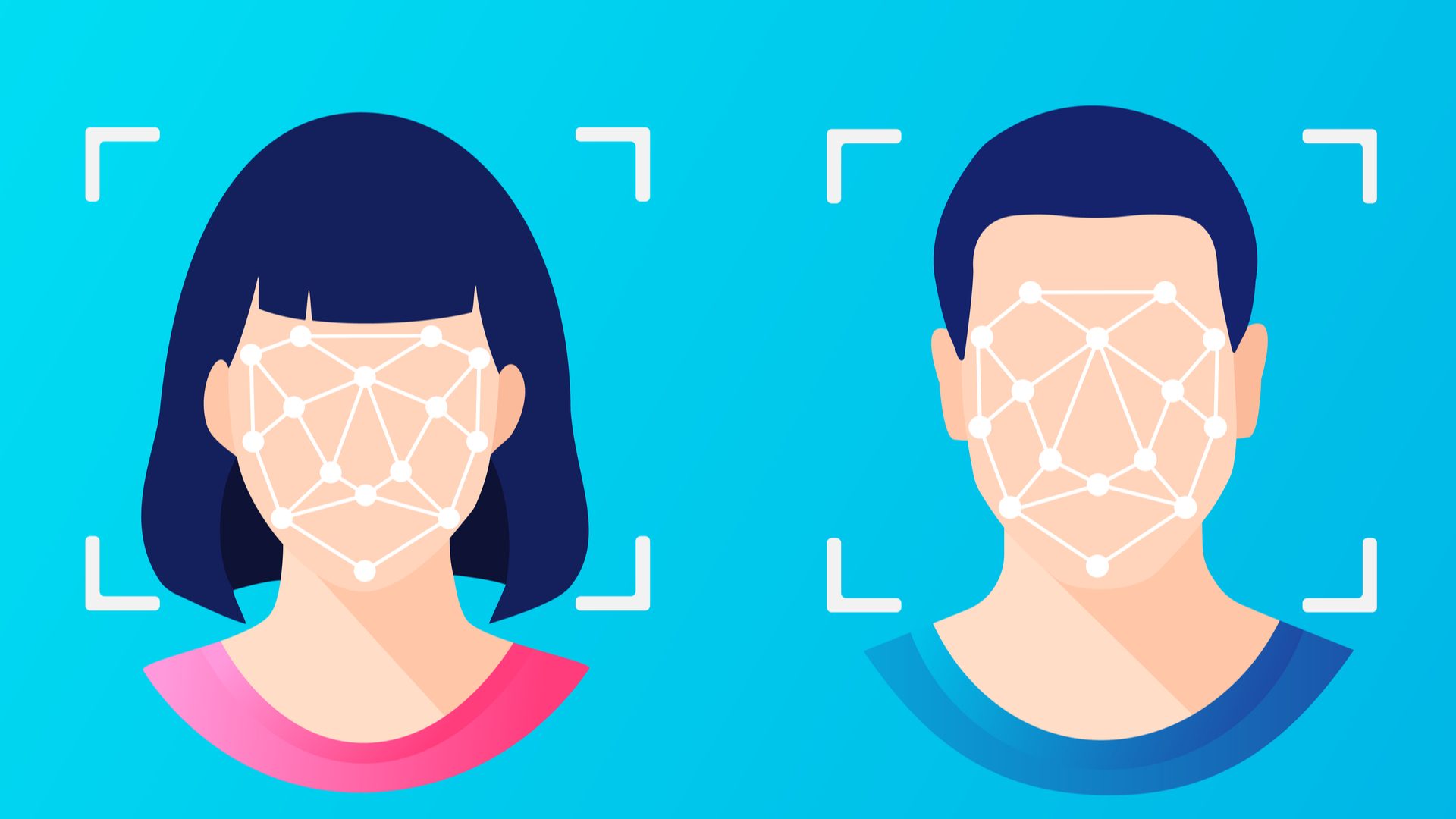
From airports to local supermarkets and mobile phone applications, facial recognition technology (FRT) has become increasingly commonplace. This advanced technology, which uses unique facial features to identify and authenticate individuals, is transforming the way we interact with the world around us. Its adoption spans various sectors, enhancing security, streamlining processes, and providing unprecedented convenience in everyday activities.
However, the rise of facial recognition technology is not without controversy, as it brings with it a host of ethical, privacy, and security concerns that fuel ongoing debates.
On one hand, facial recognition technology can make life easier and processes smoother. Many smartphones now offer facial recognition as a quick and secure login option, such as Apple's FaceID on the iPhone. In public spaces and transportation hubs, FRT can speed up security checks, reduce wait times, and improve the overall user experience. Its ability to quickly and accurately verify identities has made it a valuable tool in enhancing safety and efficiency.
However, the widespread use of facial recognition technology has also drawn criticism from various campaign groups and privacy advocates. Organizations such as Liberty and Big Brother Watch in the UK argue that this technology poses significant risks to individual privacy and civil liberties.
They raise concerns about the potential for mass surveillance, misuse of biometric data, and the possibility of unfair profiling of individuals who have not committed any wrongdoing. The fear is that, without proper regulation and oversight, facial recognition technology could lead to a society where personal freedoms are compromised, and individuals are subject to constant monitoring.
As facial recognition technology continues to advance and integrate into more aspects of daily life, it is essential to weigh its benefits against the potential drawbacks. The ongoing discussion around FRT highlights the need for a balanced approach that maximizes its advantages while addressing the ethical and privacy challenges it presents.
How does facial recognition technology work?
Facial recognition technology uses computer vision technology to extract useful information from still images or videos. This data is then analyzed by an algorithm that estimates the similarity between two faces. The algorithm considers various facial features, such as expressions and geometry. It examines several data points, including the distance between the eyes, the space between the nose and mouth, the shape of the cheekbones, and the overall length of the face from forehead to chin.
Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report - the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives

This information is transformed into a unique 'faceprint,' a set of biometric data comparable to a fingerprint. The facial recognition system can then be employed in a wide range of applications. With this understanding, let's explore the pros and cons of facial recognition technology.
Pros of facial recognition technology
Improving security systems and identifying criminals are often cited when arguing in favor of facial recognition, as well as getting rid of unnecessary labor or human interaction. However, there are also plenty of other examples.
1. Finding missing people and identifying perpetrators
Facial recognition technology is used by law enforcement agencies to find missing people or identify criminals by using camera feeds to compare faces with those on watch lists.
The technology has also been used to locate missing children. Sometimes it is combined with advanced aging software to predict what a child might look like based on photos taken when they disappeared. Law enforcement agencies often use facial recognition with live alerts to help track potential matches.

2. Protecting businesses against theft
Facial recognition is increasingly being deployed as a means of identifying known individuals before they commit crimes like theft or public affray. It's common to see CCTV in shops and places of work, and by using facial recognition software it's possible to create tools like automatic cross-referencing to match individuals to a database of known suspects.
The technology has the dual purpose of helping to prevent crime before it happens, and also – some would argue – a deterrent for would-be offenders.
If something is stolen from the business, the software can also be used to catalog the thieves for future reference.
3. Better security measures in banks and airports
Facial recognition has also come to be used as a preventative security measure in sensitive locations such as banks and airports. Similar to identifying criminals that come into shops, the software has helped identify criminals and passengers that pose a potential risk to airlines and passengers.
Border checks have also been sped up at some airports through the use of facial recognition cameras at passport-check gates.
Institutions like banks use the software in the same way to prevent fraud, identifying those previously charged with crimes and alerting the bank to watch specific individuals more carefully.

5. Drastically reduces human touchpoints
Facial recognition requires fewer human resources than other types of security measures, such as fingerprinting. It also doesn’t require physical contact or direct human interaction. Instead, it uses artificial intelligence (AI) to make it an automatic and seamless process.
It also limits touchpoints when unlocking doors and smartphones, getting cash from the ATM or performing any other task that generally requires a PIN, password or key.
5. Better tools for organising photos
Facial recognition can also be used to tag photos in your cloud storage through iCloud or Google Photos. Users who wish can enable facial recognition in their respective photo app’s settings, resulting in named folders for regular photo subjects. Facebook also used facial recognition to suggest people to tag within a photo.
6. Better medical treatment
One surprising use of facial recognition technology is the detection of genetic disorders.
By examining subtle facial traits, facial recognition software can, in some cases, determine how specific genetic mutations caused a particular syndrome. The technology may be faster and less expensive than traditional genetic testing.
7. Enhancing retail customer experiences
Facial recognition technology can also be used to personalize customer experiences in retail settings. By recognising returning customers, stores can offer personalized greetings, tailor product recommendations, and provide a more customized shopping experience.
This can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, as shoppers feel recognised and valued by the business. Additionally, it can streamline the checkout process by allowing for facial recognition payments, reducing wait times and improving overall service efficiency.
Cons of facial recognition
As with any technology, there are drawbacks to using facial recognition, such as the violation of rights and personal freedoms that it presents, potential data theft and the risk of overreliance on inaccurate systems.
1. Greater threat to individual and societal privacy
The threat of technology intruding on an individual's rights to privacy is perhaps the greatest threat created by extensive use of facial recognition.
Privacy is now a critical issue, so much so that in some cities across the likes of California and Massachusetts, law enforcement agencies are banned from using real-time facial recognition tools. Police instead are forced to rely on recorded video from tools like body worn cameras.
In 2021, then UK Information Commissioner Elizabeth Denham described the use of live facial recognition (LFR) cameras in public spaces as "deeply concerning".
2. Infringement on personal freedoms
It's just not personal privacy that is potentially at risk with mass use of facial recognition – the simple act of being recorded or scanned by the technology could discourage individuals from moving freely around their local neighborhood or city.
The argument here is that people simply do not want to feel like they are overtly being watched, judged, or recorded.
The basic premise of facial recognition is to match everyone to a database of known suspects, essentially treating you as if you are a criminal suspect without probable cause. It's a concept that some people find inherently dangerous to public freedoms.
For example, the aforementioned example of facial recognition being used to catalog potential shoplifters has led to problems for companies such as Southern Co-operative, which in 2022 faced a legal complaint for its widespread use of FRT CCTV in its shops.
3. Violation of personal rights

When used for identification purposes, facial recognition data is considered as part of the ‘special category’ of personal data under the UK's implementation of the GDPR. This also extends to racial or ethnic origin, and some facial recognition CCTV companies have been accused of.
In July 2022, a cross-party group of 67 MPs called for surveillance equipment from Chinese firms Hikvision and Dahua to be banned from use in the UK, citing concerns over ethics and security. These were informed by stories such as a report by the LA Times alleging that Dahua developed software to allow its cameras to detect Uighur minorities and issue law enforcement users with a warning upon successful detection.
4. Creates data vulnerabilities
Facial recognition also creates a data protection and cybersecurity headache. The large volume of personally identifiable information (PII) being collected and stored is an attractive target for cyber criminals, and there are already examples of hackers gaining access to such systems.
This data is particularly sensitive given that many online services, such as banking, are increasingly utilising biometric data as part of their multi-factor authentication. A threat actor with access to a database of facial data could have the tools to bypass such checks, and access even more sensitive information.
5. Provides opportunities for fraud and other crimes
Lawbreakers can use facial recognition technology to perpetrate crimes against innocent victims too. They can collect individuals’ personal information, including imagery and video collected from facial scans and stored in databases, to commit identity fraud.
RELATED RESOURCE

With this information, a thief could take out credit cards and other debt or open bank accounts in a victim’s name. In consideration of the aforementioned use of facial recognition to place shoplifters on criminal databases, threat actors could even place individuals on a criminal record.
Beyond fraud, bad actors can harass or stalk victims using facial recognition technology.
For example, stalkers could perform reverse image searches on a picture taken in a public place to gather information about their victims, to better persecute them.
Facial recognition law has lagged behind potential use by bad actors in recent years, which has prompted calls from rights groups for stricter biometrics regulations, to extend to technologies such as live facial recognition.
6. The technology is imperfect
Facial recognition is far from perfect, and cannot be relied upon to produce accurate results in place of human judgement.
The technology depends upon algorithms to make facial matches. Those algorithms are more effective for some groups, such as white men than other groups such as women and people of colour due to lack of representation within the data set on which the algorithm was trained. This creates unintentional biases in the algorithms, which could in turn translate to biases in whatever action the technology is informing, such as arrests.
In 2018, civil liberties organisation Big Brother Watch published evidence that facial recognition technology utilised by the UK's Metropolitan Police Service (MPS) was incorrectly identifying innocent people as criminals 98% of the time.
7. Innocent people could be charged
Following on from the imperfection of facial recognition, there are inherent dangers in false positives. Facial recognition software could improperly identify someone as a criminal, resulting in an arrest, or otherwise cause them reputational damage if they were to be included on, for example, a list of shoplifters.
8. Technology can be fooled
Other factors can affect the technology’s ability to recognize people’s faces, including camera angles, lighting levels and image or video quality. Mild alterations of facial data, such as a false mustache, can trick weaker facial recognition systems, while especially poor facial recognition technology could simply be tricked with a photo of a face it recognizes.
As facial recognition technology improves, its flaws and the risks associated with it could be reduced. Other technology is also likely to be used in tandem with facial recognition technology to improve overall accuracy, such as gait-recognition software.
For the time being, though, the technology’s inadequacies and people’s reliance on it means facial recognition still has much room to grow and improve.
9. Lack of transparency and accountability
One significant concern with facial recognition technology is the lack of transparency and accountability in its deployment and use. Often, the specifics of how the technology is implemented, how data is collected and stored, and who has access to the data are not disclosed to the public.
This opacity can lead to abuses of power, as there are few mechanisms in place to ensure that the technology is used responsibly and ethically. Without clear guidelines and oversight, there is a risk that facial recognition could be used for unauthorized surveillance or to target specific groups of people unfairly. The lack of transparency makes it difficult for individuals to know when and where they are being monitored, eroding trust in institutions that use this technology.
Examples of facial recognition software and apps
Although you might not know it, there’s plenty of examples of facial recognition software available on the market today. This ranges from options provided by tech giants, to software created and fine tuned by smaller companies. Here’s a selection of a few that are available on the market today, some with free options available too.
Amazon Rekognition
Amazon Rekognition is the tech giant’s computer vision APIs that you can add to your apps without needing to spend time building machine learning models. It claims to be able to analyze millions of images or videos in seconds. Some of the features include face compare and search, text detection, and video segment detection.
It has a free tier which lasts for 12 months, where you can analyze 5,000 images per month and store 1,000 face metadata objects per month for free. Its paid tier varies depending on how many images you plan to analyze per month.
FaceFirst
FaceFirst is a facial recognition platform designed for retail, law enforcement, and transportation industries. It offers features like real-time facial recognition, watchlist alerts, and demographic analysis.
FaceFirst aims to enhance security and customer experiences by providing accurate and fast identification. The pricing for FaceFirst is typically customized based on the scale and requirements of the deployment.
Face++
Face++ is a facial recognition software developed by the Chinese company Megvii. It offers robust facial detection, recognition, and analysis capabilities. Features include face comparison, face search, face grouping, and facial feature analysis.
Face++ is widely used in various applications, including mobile apps, banking, and security systems. The pricing varies based on the number of API calls and the specific features used.
Kairos
This company provides another API that developers and businesses can use to easily integrate into their software or applications. Its features include gender detection, age detection, multi-face detection, and face verification.
Pricing starts at $19 per month for the Student Cloud, while developers will pay $99 and businesses $249 per month. Each tier supports a different amount of transactions per minute, and these are priced at $0.002 per transaction.
Microsoft Azure AI Face
This allows you to embed facial recognition technology into any apps you create. The good news is that you don’t need any machine learning knowledge, you just plug in the API and you’re good to go. It contains face detection and can identify a person by matching the face to a private database or through photo ID.
It has a free tier, with 30,000 transactions free per month, or the standard tier which starts at $1 (£0.81) per 1,000 transactions up to a maximum of 1 million transactions per month.
David Gargaro has been providing content writing and copy editing services for more than 20 years. He has worked with companies across numerous industries, including (but not limited to) advertising, publishing, marketing, real estate, finance, insurance, law, automotive, construction, human resources, restoration services, and manufacturing. He has also managed a team of freelancers as the managing editor of a small publishing company.
-
 Leaked today, exploited for life
Leaked today, exploited for lifeWhitepaper How social media biometric patterns affect your future
-
 Aldi launches its first checkout-free store in London
Aldi launches its first checkout-free store in LondonNews The store uses facial age estimation technology provided by Yoti to verify the purchase of age-restricted products
-
 Facebook is shutting down its controversial facial recognition system
Facebook is shutting down its controversial facial recognition systemNews The move will see more than a billion facial templates removed from Facebook's records amid a push for more private applications of the technology
-
 EU privacy watchdogs call for facial recognition ban in public spaces
EU privacy watchdogs call for facial recognition ban in public spacesNews The EDPB and EDPS claim a ban is needed if we want to preserve our freedoms and create a human-centric legal framework for AI
-
 NatWest trials voice banking in the UK
NatWest trials voice banking in the UKNews Customers will be able to use a Google Home to access their accounts

