Best web browsers 2023: Firefox vs Google Chrome vs Microsoft Edge
Firefox vs Chrome vs Edge - discover which comes out on top in the ultimate battle to crown the very best browser


Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report - the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Like anything else you do on your computer, be it editing documents or productivity tracking, browsing the web should be done with the best tools available. Every computer is shipped with a default browser and each operating system (OS) is preloaded with a proprietary browser, but these may not be the best for each individual’s specific needs. Different browsers will prioritize different features, and some features will be exclusive to each browser itself.
Trying to weigh up Firefox vs Chrome vs Edge can be a daunting challenge, and every major browser will usually offer features that will satisfy the needs of most internet users. Nonetheless, the competition would not be so heavy if slight differences did not matter to users. Choosing the right browser for you is a difficult decision and migrating browsers can be a long and tedious process. As such we recommend carefully considering your decision before committing to any in order to ensure your initial time investment is worth it.
What to look for in a browser
Before you make your choice, we recommend you research the core features of each browser to determine what you are looking for. Many features will be shared across Firefox, Chrome, and Edge, including password managers and private browsing. But other features may be exclusive to the specific browsers and these features require the closest consideration.
Take, for example, Firefox, which uses less RAM than its competitors and is therefore less computationally demanding to run. This might mean it is the better choice for people with hardware with low RAM, or who require RAM for other tasks and do not want their internet browsing to drain this resource.
Microsoft Edge features Copilot integration, one component to Microsoft’s wider push to bring generative AI to all of its major products in order to bring richer, smarter, and quicker user experiences.
Google Chrome is easily the most popular browser on the market and includes a number of helpful features such as offline document editing if you use the Google Workspace on a daily basis.
A number of organizations have their own in-house extensions and web apps that staff rely on to complete their work. Sometimes, these are only compatible with specific browsers, meaning the number of options you can pick from may be restricted to those that support the extension.
Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report - the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
The nature of your work is also a factor that will influence your decision. Developers who work with metaverse experiences, for example, may choose the Firefox Reality browser in order to navigate the web using a VR headset.
Finally, regardless of the bold claims made by each browser about their security and privacy credentials, you will want to confirm that your choice is compliant with your employer’s IT policies. When working remotely, you might need to speak with your administrator to ensure your browser is able to join the network. We would be very surprised if any of our choices cause any consternation, but forewarned is forearmed.
Understanding Chrome vs Chromium vs ChromeOS
You’ll see “Chrome” and “Chromium” used a lot in this roundup. It’s not a misprint - they’re two separate browsers... except they’re not. Let us explain.
Released alongside the flagship browser in 2008, Chromium is a totally open-source, white-lable version of Chrome. Most of the codebase is the same, and although Google curates the project, it is separate from parent company Alphabet LLC. Chromium’s logo is identical to that of Chrome, just with a blue and grey colour scheme, instead of Google’s traditional colors. The UI is completely identical, but Chromium does lack some codecs and syncing technology which is standard in the proprietary version of Chrome.
Chromium is an important browser to be aware of because of its role as the basis for many of the other browsers on the market, including Microsoft Edge, Opera, and Vivaldi. Thanks to the open source community, Chromium is available for more unusual machines such as the Raspberry Pi; and creators of browsers based on a ‘forked’ build of Chromium are expected to add their code to the Chromium codebase for the benefit of all. Stock browsers for Android forks such as Samsung (Samsung Internet) and Amazon (Silk) are usually based on chromium.
Chrome is Google’s official build of Chromium and the most popular browser in the world. It has tighter integration with Google accounts and a number of additions “under the hood”. It has three ‘channels’ - Stable, Beta, and Canary - with each updated to a new official build on a four-week cycle.
ChromeOS, meanwhile, is another separate yet related entity. It's an operating system built on the Chrome browser and used in Chromebooks and other Google desktop products; almost identical to the Chrome browser, but with a desktop, settings, and driver support. As of February 2022, you can also install it on PCs and Macs, via ChromeOS Flex.
All three products share the same codebase and are completely compatible with Chrome’s wide range of extensions. Updates to ChromeOS also run on a four-week cycle, but often arrive several days later than the standalone Chrome browser.
Best browsers 2023: Edge vs Chrome vs Firefox
Google Chrome
The growth in market share for Google’s browser since launch has been phenomenal. During 2021, Statcounter reports that 63.84% of devices around the world were running it, and at one point that figure was over 70%. There’s a lot to love about Chrome - most notably its tight integration with Google services making it extremely easy to switch between devices, as well as a huge ‘Chrome Store’ full of extensions, apps and customizations. As the world’s most popular browser, it has almost complete compatibility with any webpage you can throw at it and renders them at speeds unimaginable even a decade ago.
All that speed comes at a cost, though. Chrome is a notorious resource hog, using over a gigabyte of RAM during runtime. Add a few extensions and you could find it monopolizes the bulk of your machine’s memory. Google has worked hard to bring down Chrome’s memory footprint, but it’s still a lot more resource-hungry than any other browser on this list.
Despite this, Chrome is still the people’s choice by a factor of three and if there’s a feature not available natively, the chances are someone has written an extension to add it. Just remember that more extensions equals more RAM usage, so if you’re running a 2GB netbook, you might want to rethink how many you add.
Chrome is available on Windows, macOS, most Linux distros, Android, iOS, and Chromebooks (as part of ChromeOS).
Microsoft Edge
Technically, the current product calling itself Microsoft Edge should be called Edge 2. When it launched back in 2016 it looked very different and owed much of its layout to its predecessor, Internet Explorer. It failed to capture the public’s imagination, so it was completely rebuilt from the ground up using the Chromium codebase, and from April 2021 that became the only version of Edge, pre-installed alongside Windows 10 or 11.
It differs from Google’s Chrome in a number of ways, not least of all that it’s slightly less of a memory hog. It’s compatible with a limited number of extensions originally designed for Chrome, but Microsoft controls which ones. This is supposedly due to security concerns, but ironically it’s the browser that collects the most user telemetry, leading some experts to question its own security. Users still report compatibility issues with extensions, which is a good point to remind ourselves that Edge, in its current form, is only two years old and occasionally shows its relative lack of bug-squashing.
Where Chrome links up nicely with Google products, as you’d expect, Edge syncs with your Microsoft account. Being a Microsoft product, it’s very keen to enforce Bing on you, which takes a certain amount of tweaking to change and in some cases (such as translation) can’t be switched to another provider.
There’s no question that Chromium Edge is a great deal better than the legacy version and yes, for basic tasks, it’s a little less power-hungry than Chrome, but the fact that it uses Bing so liberally whilst having relatively poor extension support means there’s still no reason not to download Chrome at the first opportunity. The fact that in 2021, it only garnered 3.99% of the market, despite being preinstalled on Microsoft products, speaks volumes. It’s a good browser, but it’s young, and it’s not quite there yet.
Mozilla Firefox
An open-source project, originally designed for use by Mozilla’s development team, Firefox is the oldest of the ‘big three’ browsers - in fact in 2022, it’s celebrating its 20th birthday. Before Chrome arrived, it was gaining significant market share. After several years in the relative doldrums, it was retooled in 2017 under a project called ‘Quantum’ which allowed its proprietary Gecko engine to perform at speeds more akin to Chrome.
Firefox was the first browser to offer extensions, which it refers to as 'Add-ons', and as a result, it had a wealth of them to download, but since Quantum it has relaunched the feature and this treasury has been replaced by a new library which is still growing. The new add-ons use the same API as Chromium and as a result, there is now some cross-compatibility.
In recent years, Firefox has focused on its security credentials and in 2021 became the first browser to offer the ability to block cross-site tracking. It also offers DNS over HTTPS (DoH), a feature that makes it almost impossible for hackers to monitor your web traffic, and a feature that blocks any scripts that attempt to mine cryptocurrency from your machine.
Firefox is still a great browser, but with Chromium-based browsers so much the norm now, it has seen its popularity plummet from nearly 30% at one time, down to 3.91% in 2021, putting it almost exactly on par with Edge. Whilst it still has a lot to recommend it both in terms of security and performance, Mozilla has consistently been last to basic features (it only began sandboxing processes in 2018) that are standard in other browsers. However, if you’re looking for a corporate deployment to your whole team, there is a long-term support edition available alongside tools to push itself to multiple machines on a domain, making it a smart choice for business.
Apple Safari
Although we’re focusing on Windows browsers for this round-up, we can’t ignore Apple’s stock Safari browser, which has 19.56% of the market, almost entirely made up of Mac and iPhone/Pad users after Apple ceased updating the Windows version a decade ago. For macOS and iOS users, it offers a more familiar layout and continuity features that let you carry on your surfing from exactly where you left off on another Safari instance, as well as a handful of unique software features built on integrations with the rest of the macOS platform.
Mac and iOS users should be aware, however, that all the browsers on this list are rendered using Apple Webkit rather than the standard renderer (usually Blink) in order to comply with Apple’s policies. As such, you’ll find that performance between browsers is much of a muchness, and any desire to switch to something other than Safari should be based on features, rather than any hope of a performance boost.
Best browsers 2023: Head-to-head performance
Just because the majority of the options above share the same Chromium codebase, it doesn’t mean they’ll have identical performance. In our benchmarking tests, we used three tools - Jetstream 2.0 which measures Javascript and WebAssembly performance using advanced web apps, Speedometer, which shows web app responsiveness, and Kraken, which calculates Javascript, but based on what Mozilla calls “more realistic workloads”.
The results were surprising. You may remember a few years ago, all the major browsers claimed that it was theirs that offered the fastest performance. Our results explain why - there simply is no clear winner. While Chrome offered a blistering 62.619 in the Jetstream tests, compared with a pitiful 35.182 for Firefox, Speedometer results were so poor at 19.5 that we reran the test several times to make sure it really was that bad. Compare that to Microsoft Edge at 69.1, with Opera a valiant second at 66.2. Kraken, a tool created by Firefox maker Mozilla, actually proved a problem for its own browser - it gave the slowest result of 3967.1ms. The winner was Vivaldi, which scored 1618.6, more than twice as fast as Firefox - yet scored mid-table on our other benchmarks.
By aggregating the results, we’re declaring that Opera is the best-performing browser by some margin, coming a consistent runner-up in all our benchmarks. Microsoft Edge is next, followed by Vivaldi, Brave and bringing up the rear, Chrome in fifth place, thanks to its perplexingly poor Speedometer performance, and Firefox bringing up the rear.
It’s worth remembering though, that none of these scores indicate a problematic or unusable level of performance, and we found that all our browsers (with the exception of Opera) were better at some tasks than others - so it may be that for your workload, another browser could be the right one for you.
Edge vs Chrome vs Firefox: Which is best?
In the internet’s early days, there was a clear benefit to staying with the default browser on the operating system. These days, however, the essential task of a web browser – to browse the web – is a mostly universal experience regardless of which you choose. As such, before choosing the right browser for you you should pay attention to the feature set of each – whether that be compatibility with other products, a lightweight footprint, or one of the unique features of the smaller browsers.
In the majority of instances, add-ons or extensions will let you gain any features that aren’t natively supported. We can’t say any one browser is the perfect fit for everyone (but if you push us, Chrome is the best of most worlds) so we would recommend trying a few options and creating your ideal surfing environment.
Best browsers 2023: Google Chrome alternatives
If you enjoy Chrome’s user experience, but don’t particularly want to fuel Google’s data-hungry business model, there are various alternatives to the major players of internet browsing that provide some intriguing comparisons.
Opera

Of all the Chromium browsers, Opera is the one that looks most visually distinct from Chrome. As one of the first browsers to switch to Chromium from its own engine, back in 2013, it has had ample time to carve a distinctive path, and has done so in spades. With a free VPN and Ad-Blocker built-in, you’d be forgiven for thinking they’d done enough, but with “Speed Dial” access to your favorite sites from a mosaic of thumbnails, a built-in crypto wallet, a sidebar for social media, and a variety of instant messaging platforms, and a one-click eraser for all your cookies and browsing history, Opera is an absolute powerhouse.
Unfortunately, its add-ons aren’t directly compatible with Chrome extensions, but there is an unofficial way to add them. The big turn-off for Google users is that it syncs with other instances of Opera, but not with Google (or Microsoft) accounts. It’s not a dealbreaker, but you’ll notice the lack of this feature if you’re used to it. It’s a shame because in most other ways, Opera is very, very special.
Vivaldi

A relative newcomer, Vivaldi is the product of John Van Teschiner, one of the architects of the original (pre-Chromium) Opera. Originally designed to replace some features retired from his old browser, Vivaldi has blossomed into a distinct product in its own right, offering stackable tabs groups, tracking protection through DuckDuckGo, a pop-out video player, native mail and calendar clients and Chromecasting support, to name but a few. Vivaldi has become more like a dashboard for everything you’re doing, meaning you could, in theory, never leave it for another app all day. It’s also very privacy and safety-minded, with granular controls over blocking of ads and cookies by type, content, or source.
Brave
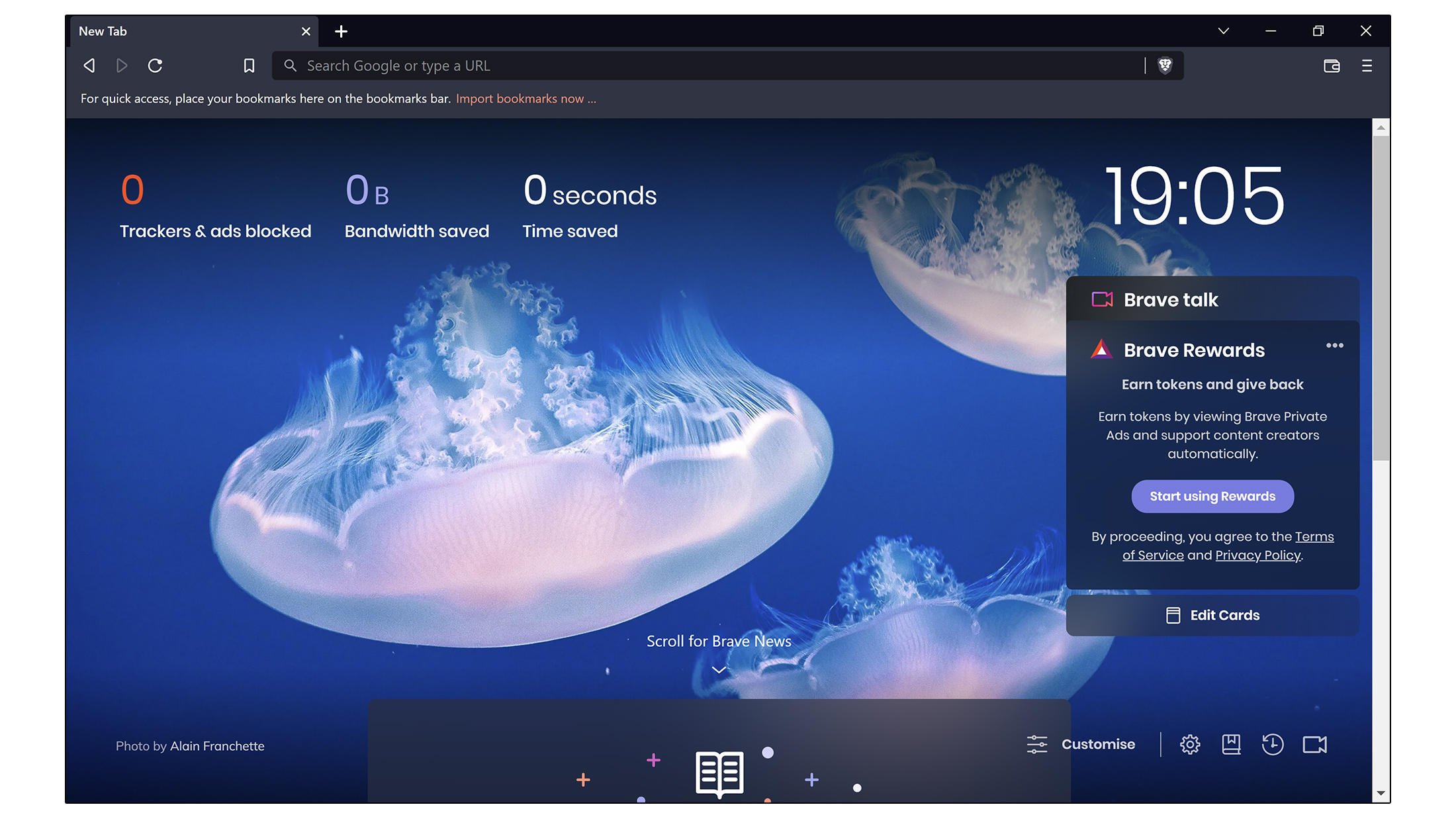
Brave is a privacy-first browser with a twist - by default it will block ads, but if you switch them on, you can earn cryptocurrency for each one you watch. It has repeatedly come top in “most private browser” testing, but it also has some unique features - for example if you try and surf to a page that doesn’t exist, it will automatically search for a cache from Wayback Machine. If you need further privacy, you can route traffic through the TOR network and it also has its own in-built news aggregator. You can use cryptocurrency earned to offer micropayments to bloggers on certain sites, a reflection of Brave’s attempts to try and find new ways to finance the internet. There’s a lot to love (perhaps too much) and from a business point of view, you might find it a bit “busy”, but as a product in its own right, it’s a promising new alternative.
What about Internet Explorer?
Due to being included with every version of Windows since Windows 95, Internet Explorer is familiar to most computer users. Despite ceasing active development of Internet Explorer in 2016 to focus on its Edge browser, it continued to bundle the final edition IE11 with Windows to allow compatibility with legacy sites.
This all changed in 2022, when on June 15th, Internet Explorer was put out to pasture, once and for all. Going forward, Microsoft recommends using Edge (of course), which offers an Internet Explorer emulator mode that can be opened in a new tab. This should only be used for web pages that are business-critical, and only as a stopgap until your organization upgrades the page or package in question to be compliant with more modern alternatives.
Some products which already bundle Internet Explorer, such as Windows Server, won’t reach EOL until 2029, so Microsoft will continue to offer IE security updates until that time - but it bears repeating that in 2022, the use of IE really should be a last resort. There’s a joke in the tech industry that 'Internet Explorer is the browser you use to download Chrome'. It’s funny because it’s true.
Darien began his IT career in the 1990s as a systems engineer, later becoming an IT project manager. His formative experiences included upgrading a major multinational from token-ring networking to Ethernet, and migrating a travelling sales force from Windows 3.1 to Windows 95.
He subsequently spent some years acting as a one-man IT department for a small publishing company, before moving into journalism himself. He is now a regular contributor to IT Pro, specialising in networking and security, and serves as associate editor of PC Pro magazine with particular responsibility for business reviews and features.
You can email Darien at darien@pcpro.co.uk, or follow him on Twitter at @dariengs.
-
 CISOs are keen on agentic AI, but they’re not going all-in yet
CISOs are keen on agentic AI, but they’re not going all-in yetNews Many security leaders face acute talent shortages and are looking to upskill workers
-
 Why Amazon’s ‘go build it’ AI strategy aligns with OpenAI’s big enterprise push
Why Amazon’s ‘go build it’ AI strategy aligns with OpenAI’s big enterprise pushNews OpenAI and Amazon are both vying to offer customers DIY-style AI development services
-
 Spanish spyware outfit uncovered, develops exploits for Windows, Chrome, and Firefox
Spanish spyware outfit uncovered, develops exploits for Windows, Chrome, and FirefoxNews Google was only able to discover the company after an anonymous submission was made to its Chrome bug reporting programme
-
 Lenovo IdeaPad Duet 5 Chromebook review: A confident convertible
Lenovo IdeaPad Duet 5 Chromebook review: A confident convertibleReviews A gorgeous display, superb battery life and Surface Pro-style form factor all lift the Duet 5 above its rivals
-
 Firefox 95 boosts protection against zero-day attacks
Firefox 95 boosts protection against zero-day attacksNews Mozilla's browser now takes a more granular approach to walling off code
-
 Mozilla to end support for Firefox Lockwise password manager
Mozilla to end support for Firefox Lockwise password managerNews Replacement service already lined up as browser specialist continues to streamline business
-
 Firefox available on Microsoft Store for first time
Firefox available on Microsoft Store for first timeNews Gecko-based browser arrives after Microsoft removes restrictions
-
 How to take a Chrome screenshot
How to take a Chrome screenshotTutorials Learn how to take a screenshot in Chrome with and without extensions
-
 Why I’m leading a browser double life
Why I’m leading a browser double lifeOpinion There are benefits to using more than one browser
-
 Mozilla fixes two Firefox zero-days being actively exploited
Mozilla fixes two Firefox zero-days being actively exploitedNews Critical vulnerabilities allow attackers to execute arbitrary code or trigger crashes
