The four major software development lifecycle models and how they work
We explain each of the four main software development lifecycle models in detail, outlining their advantages and disadvantages

The software development lifecycle (SDLC) in software engineering is a methodology that defines the logical steps for developing a custom software product. This methodology is used to structure, plan and control the software development process.
In simple terms, we can define SDLCs as a series of separate methodologies that a developer can use to standardise the process of software development. A number of SDLC models are available, but choosing the right one is no easy task: and with enterprises relying on software, it's key to ensure that the correct model is chosen and taken forward.
In this article we'll try to highlight the main advantages and disadvantages of some commonly-used SDLCs.
1. Waterfall model
This is one of the simplest, classic life-cycle models, also known as the "linear-sequential" life cycle model. In a waterfall model, each phase must be completed before moving onto the next. A review process is scheduled at the end of each phase to check that the project is on the right track. The steps are as follows:
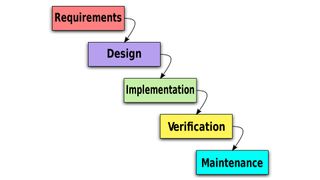
Advantages of the waterfall model
- Simple to understand and use
- Each phase is independent of other phases, and is processed and completed separately
- Suitable for smaller projects, and for projects where the requirements are clearly outlined
Disadvantages of the waterfall model
- No output or working software is produced until late in the lifecycle
- High degree of uncertainty and risks
- Not a good choice for big or ongoing projects
2. Iterative model
The Iterative model can be thought of as a “multi-waterfall” cycle. Cycles are divided into smaller and easily managed iterations. Each iteration passes through a series of phases, so after each cycle you will get working software.
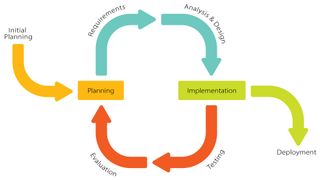
Advantages of the iterative model
- Produces working software early during the lifecycle
- More flexible, as scope and requirement changes can be implemented at low cost
- Testing and debugging is easier, as the iterations are small
- Low risk factors, as the risks can be identified and resolved during each iteration
Disadvantages of the iterative model
- This model has phases that are very rigid and do not overlap
- Not all the requirements are gathered before starting the development; this could lead to problems related to system architecture at later iterations
3. Spiral model
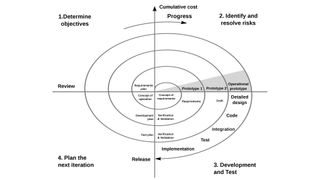
The spiral model is similar to the iterative model, but places more emphasis on risk analysis. The steps involved in this model can be generalised as follows:
- System requirements are defined in as much detail as possible by involving various users, so as identify the various aspects of the system
- A preliminary design of the system is created; this is the most crucial step in the spiral model, as it helps in developing cost-effective strategies for working on a project
- Using the preliminary design, a prototype for the new system is developed; this is generally a scaled-down system, which represents an approximate characteristics of the final output
Consecutive prototypes are then evolved through a fourfold procedure:
Get the ITPro. daily newsletter
Receive our latest news, industry updates, featured resources and more. Sign up today to receive our FREE report on AI cyber crime & security - newly updated for 2024.
- Strengths, weaknesses and risks of the previous prototype are evaluated
- Requirements for the new prototype are defined
- Planning and design of the new prototype begins
- Developing and testing the new prototype are carried out
Advantages of the spiral model
- Good for large and critical projects
- Working software is produced early during the lifecycle
- Large amount of risk analysis
Disadvantages of the spiral model
- Involves higher cost
- Not suitable for smaller projects
- Project success depends on the risk analysis phase; hence, it requires highly specific expertise in risk analysis
4. Prototype model
The prototype model is used to overcome the limitations of the waterfall model. In this model, instead of freezing the requirements before coding or design, a prototype is built to clearly understand the requirements. This prototype is built based on the current requirements.
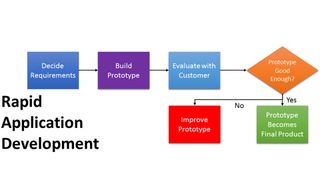
Through examining this prototype, the client gets a better understanding of the features of the final product. The processes involved in the prototyping approach are shown in the image above.
Advantages of the prototype model
- Benefits from user input
- As a working model of the system is provided, users get a better understanding of the system that is being developed
- Errors and risks can be detected at a much earlier stage, as the system is developed using prototypes
Disadvantages of the prototype
- Increases complexity of the overall system
- Involves exploratory methodology, and therefore involves higher risk
- Involves implementing and then repairing the way a system is built, so errors are an inherent part of the development process
Software development lifecycles: Summary
Across these four common models, you can see the variety in approach to software development lifecycles, with different levels of process applied. As with all development, quality assurance is key when it comes to software, and aligning development goals with business strategy is integral to a smoother process.
Will was previously US and Ecommerce Editor at IT Pro, and before that B2B editor for ecommerce with a particular focus on IT Pro Portal, alongside responsibilities on Tom's Guide and TechRadar Pro for certain verticals.
Having been a sub editor, associate editor, and deputy editor at a global B2B publication, and editor of a B2B membership journal, he has over 12 years of editorial experience in the sector, spanning online content and magazine production. In his spare time, he writes film and video game reviews.





