Command Prompt Windows 10: What is it and how does it work?
We take a look at one of the most basic - and most powerful - features in Windows 10

Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report - the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
When it comes to navigating a Windows machine, most professionals will swear by the command prompt function.
There is a certain level of technical know-how needed for it and any self-respecting IT professional should really find the time to fully understand the command prompt. You can't really call yourself a 'pro' without it.
Once mastered you might start referring to it in more common terms - simply 'CMD' - and it will quickly become your go-to method for either Windows 10 and Windows 11. It can be used to create shortcuts to pin to the taskbar, access vital information about the computer and even manage security issues.
Users should think of the command prompt as a more powerful alternative to the graphical user interface. The main difference is that it doesn't hide its functions or bury them under layers of the menu. Such is the brilliance of command prompt, Microsoft has virtually left its design unchanged since 1987.
What is the command prompt?
On Windows machines, the command prompt is used to action a variety of different tasks, such as automating scripts or finding batch files. It's also a handy tool for fixing faults in Windows.
Aesthetically the command prompt leaves a little to be desired. It looks very much like an advanced navigation tool built by developers - which is probably why the uninitiated fear it so much. However, it can be mastered with a little trial and error. Just take it at your own pace and you'll eventually master it. Once it is under your grasp, you'll never use a computer in the same way again.
How to open the command prompt
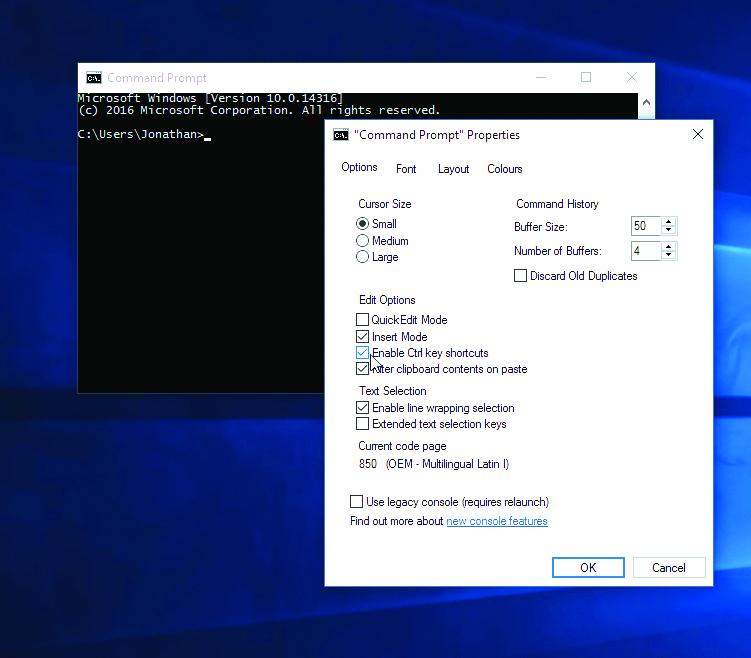
There are many different ways to open the program, the simplest of which involves simply typing 'command prompt' or 'cmd' into the Windows 10 search bar and it will be the top result. If you like your keyboard shortcuts, Windows+X will open the Power Users menu from which command prompt can be launched with one click.
Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report - the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
If you want to make serious changes to your system using command prompt, you'll most likely have to run as administrator. This can be done in either of the previous two methods by either right-clicking the icon in search or by selecting the admin option from the Power Users menu.
Any major changes to the system made with command prompt will likely require you to run it as an administrator. To do this, right click the icon in the search bar or on the taskbar and select 'run as administrator.'
It can also be done through Task Manager: simply open it up, open the 'File' menu and CTRL+click 'Run New Task' to immediately launch command prompt as administrator.
How does the command prompt work and why would you use it?
The command prompt works at a more basic level than Windows, but that is not to say it isn't powerful. It means you gain more control over the PC and communicate with it in a more direct way.
Common cmd commands include ‘dir’, which lists an alphabetised list of files in each directory, ‘cd’ which changes the current working directory, and ‘copy’ which copies files from one directory to another. Command prompt can perform tasks such as shutdown the system ('shutdown /s'), and also be used to access parts of the operating system that are not available through the graphical user interface.
In addition to the commands mentioned above, there are a number of other useful commands such as ipconfig (which shows what IP address a computer has), Tracert (which shows information on each step between the computer and a target host elsewhere on the internet such as a website), and the system file checker (sfc), which finds any corrupt or missing files, and automatically replaces them using cached copies kept by Windows.
What about Windows PowerShell?
Ever since the Windows 10 release, Microsoft has been attempting to get users to abandon the legacy command shell and opt for a new alternative – PowerShell.
First released as an optional component in 2006, PowerShell boasts an abundance of useful commands, also known as cmdlets, which were designed to be better integrated with most Microsoft offerings. As functions that exist inside compiled DLLs on a system, the main purpose of cmdlets is to not only become a more modern substitute for the Command Prompt, but also batch files and VB scripts.
More information on how PowerShell compares to CMD can be found here.
When Microsoft’s Windows 11 was released in 2021, Microsoft soon announced plans to make Windows Terminal the default command-line experience, with PowerShell the recommended interface rather than cmd.
However, not all is lost: command prompt fans will likely be able to change their default command shell in the system settings, and Microsoft isn’t completely dropping the tool from Windows 11 any time soon.

Clare is the founder of Blue Cactus Digital, a digital marketing company that helps ethical and sustainability-focused businesses grow their customer base.
Prior to becoming a marketer, Clare was a journalist, working at a range of mobile device-focused outlets including Know Your Mobile before moving into freelance life.
As a freelance writer, she drew on her expertise in mobility to write features and guides for ITPro, as well as regularly writing news stories on a wide range of topics.
-
 Windows 10 end of life has passed – here's your business guide to Windows 11
Windows 10 end of life has passed – here's your business guide to Windows 11In-depth As Windows 10's mainstream support ends, it's time for businesses who have yet to upgrade to take a second look at Windows 11
-
 Windows 10 end of life could create a major e-waste problem
Windows 10 end of life could create a major e-waste problemNews The study marks the latest Windows 10 end of life e-waste warning
-
 Windows 10 extended support costs could top $7 billion
Windows 10 extended support costs could top $7 billionNews Enterprises sticking with Windows 10 after the October deadline face huge costs
-
 A senior Microsoft exec says future Windows versions will offer more interactive, ‘multimodal’ experiences
A senior Microsoft exec says future Windows versions will offer more interactive, ‘multimodal’ experiencesNews With speculation over a Windows 12 reveal mounting, a senior company figure claims the new operating system will mark a step change for users
-
 Microsoft’s botched August updates wiped SSDs, now it’s breaking PC resets and recoveries on Windows
Microsoft’s botched August updates wiped SSDs, now it’s breaking PC resets and recoveries on WindowsNews An out-of-band patch has been issued by Microsoft to fix a flaw introduced by its August update
-
 A Windows 11 update bug is breaking SSDs – here’s what you can do to prevent it
A Windows 11 update bug is breaking SSDs – here’s what you can do to prevent itNews Users first began reporting the Windows 11 update bug last week
-
 The Windows 11 migration conundrum: What role can the channel play?
The Windows 11 migration conundrum: What role can the channel play?Industry Insights Resellers are instrumental to making the right choice about the next steps...
-
 The NCSC just urged enterprises to ditch Windows 10 – here’s what you need to know
The NCSC just urged enterprises to ditch Windows 10 – here’s what you need to knowNews The UK cyber agency says those that haven’t migrated to Windows 11 should do so immediately

